Correlating the non-linear time series and spectral properties of IGR J17091-3624: is it similar to GRS 1915+105?
Using the correlation integral method, we explore the non-linear properties of black hole sources IGR J17091-3624 by comparing the underlying behaviour to GRS 1915+105. We find that while GRS 1915+105 is known to reveal a combination of fractal (or even chaotic) and stochastic behaviours, IGR J17091-3624 mostly shows stochastic behaviour. Therefore, although several observations find […]
Interactions between emotion, motivation, and cognition.
Throughout our lives, emotional and/or motivational factors influence our thoughts and actions. Hence, there is a clear need to understand how emotion, motivation, and cognition interact in the human brain. Knowledge of brain mechanisms underlying these interactions is not only relevant to our healthy lives but also has potential clinical relevance. In mental disorders such […]
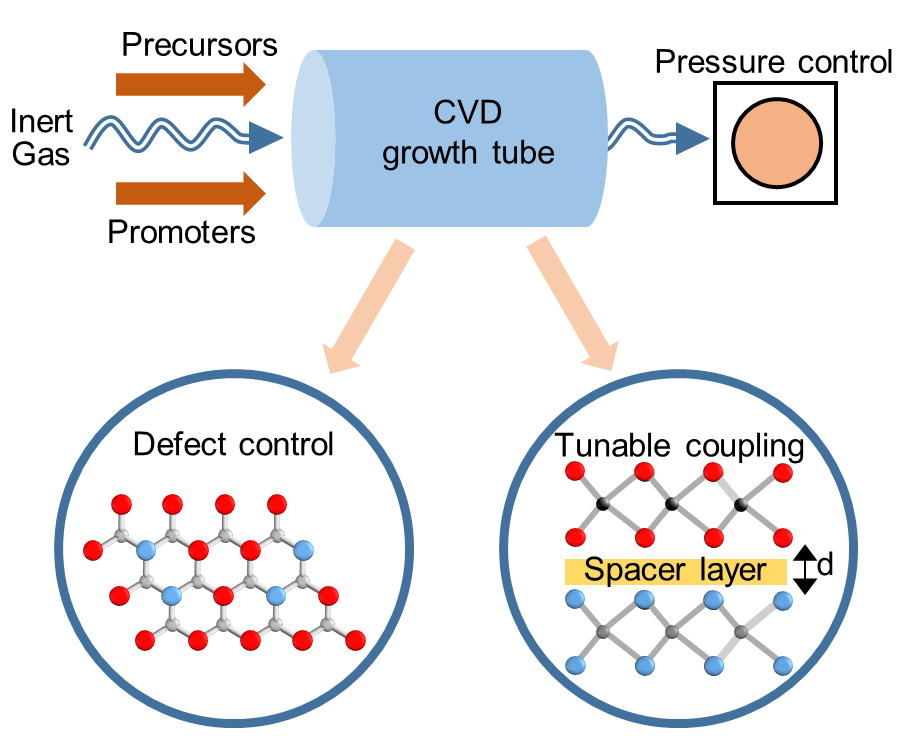
Materials for neuromorphic computing
Defects in TMDs (vacancies, substitutional atoms) have been proposed for optical memories and neuromorphic computing. Chemical vapour deposition (CVD) is a synthesis process that allows controllable defect control by careful tuning of process parameters. We are exploring the use of different growth environments (gases, solid or gaseous precursors), as well as after-growth cooling rates to […]
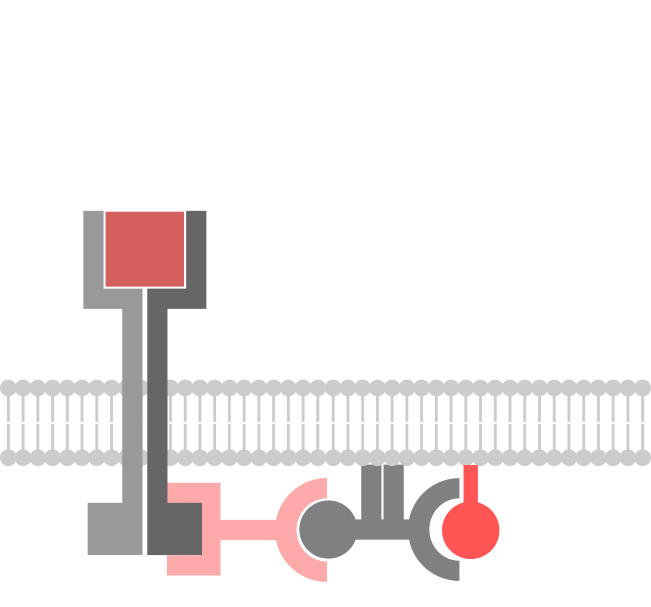
Spatiotemporal organization of cell signaling
Cells use a set of molecular processes, called cell-signaling, to recognize and respond to stimuli. Cell-signaling processes work together to sense the outside world by recognizing, processing, and transmitting signals within and outside a cell. Most of these processes require the molecules within the cell to organize in specific fashion in various cellular locations, which […]
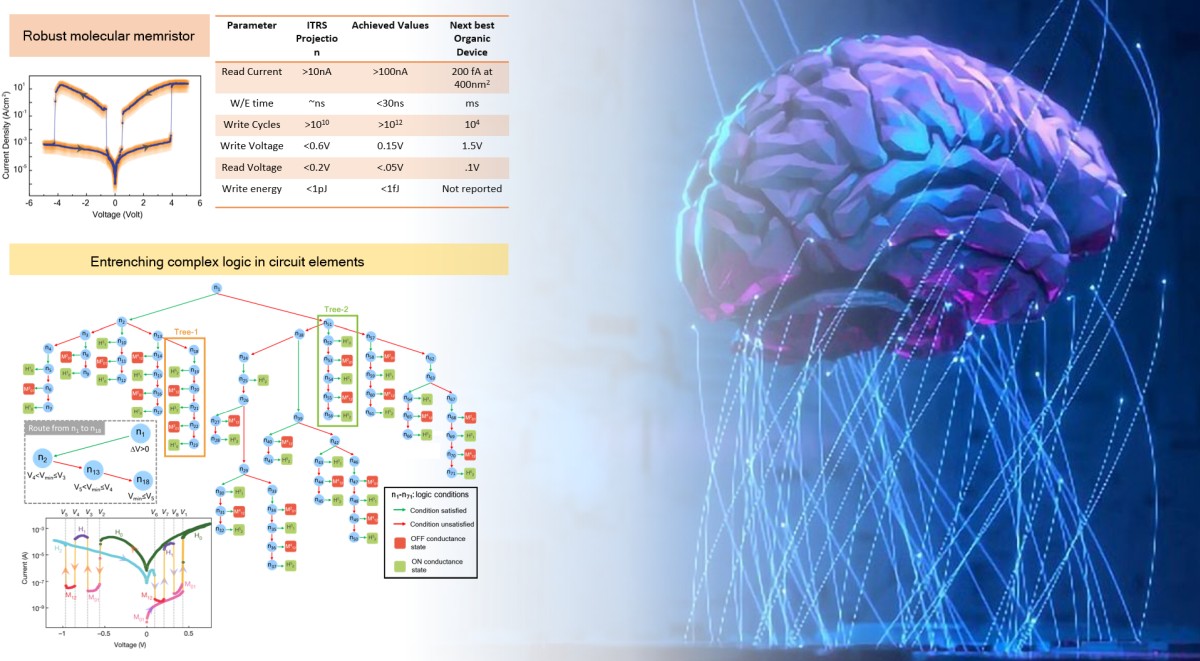
Capturing brain inspired functionalities in molecular circuit elements
We are designing molecular circuit elements that capture intelligence, cognition and decision-making ability at nanoscale material properties. Our aim is to come up with devices that can operate on the verge of chaos and offer the maximum training efficiency with a minimum energy consumption. Faculty: Sreetosh Goswami References: Sreetosh Goswami*, Rajib Pramanick, Abhijeet Patra, et.al. […]
Cross-Modal Retrieval
In IACV Lab, we work on various applications in Computer Vision and Machine Learning, one area being cross-modal matching. Due to increase in the number of sources of data, research in cross-modal matching is becoming an increasingly important area of research. It has several applications like matching text with image, matching near infra-red images with […]
Large scale computational model of fusion plasmas
The main focus of our research group is on neural network assisted large scale computational model of fusion plasmas. This research project aims to provide detailed insights into tokamak plasma stability using advanced numerical simulations and is aligned with the mainstream R&D program of ITER. ITER is the largest experimental fusion reactor being constructed presently […]
Homogeneous Length Functions on Groups: Intertwined Computer and Human Proofs
This work was an interplay between human and computer proving which played a role in the discovery of an interesting mathematical result. The unusual feature of the use of computers here was that a computer generated but human readable proof was read, understood, generalized and abstracted by mathematicians to obtain the key lemma in an […]
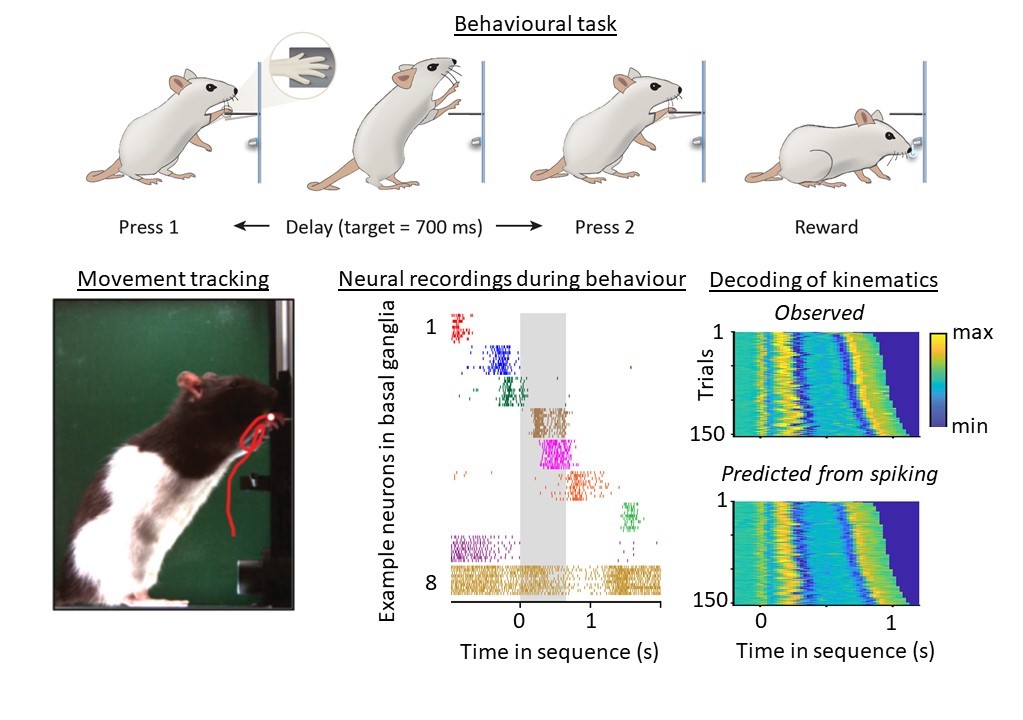
The basal ganglia control the detailed kinematics of learned motor skills
The basal ganglia are known to mediate action selection, but whether and how they contribute to specifying the kinematics of learned motor skills is not understood. We probed this question by recording and manipulating basal ganglia activity in rats trained to generate complex task-specific movement patterns with rich kinematic structure. We found that the basal […]
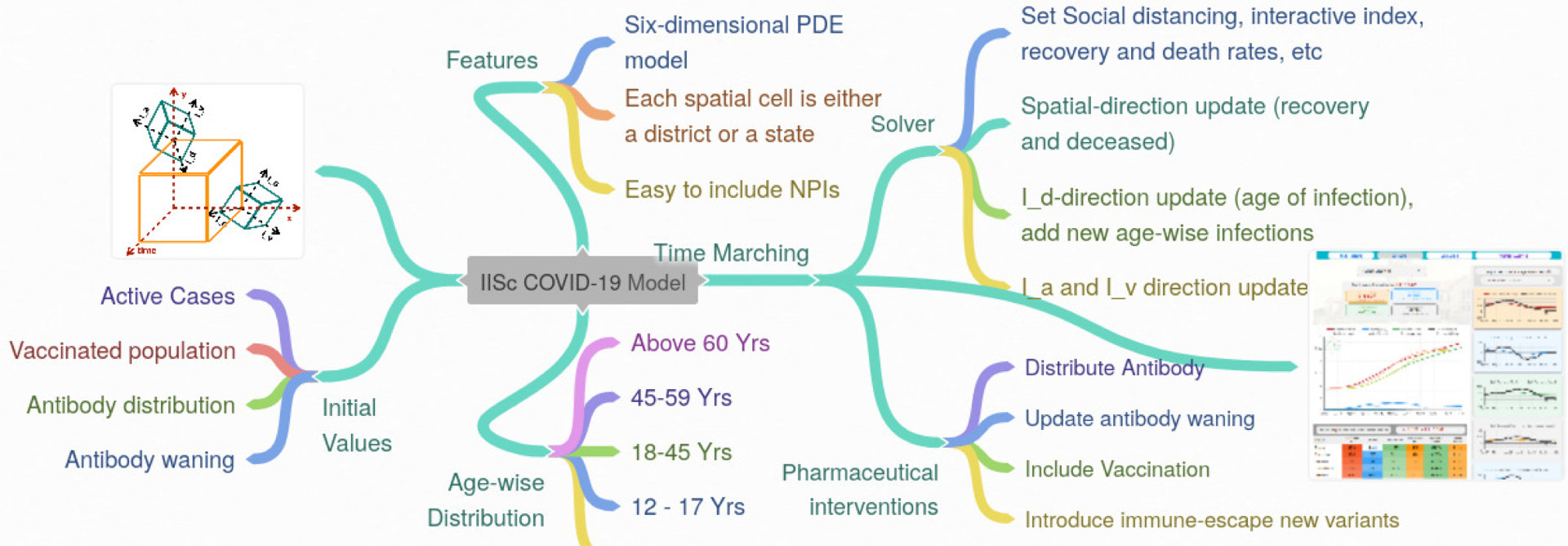
Prognostic estimates and scenario analysis of COVID-19
A novel predictive modeling framework for the spread of infectious diseases using high-dimensional partial differential equations is developed and implemented. Prognostic estimates of Covid-19 spread using a six-dimensional (time, 2D space, infection severity, duration of infection, and population age) modelled in this framework. These insights have been used by local states to frame science-informed policies. […]
Arnab Barik
Stepping barefoot on a pin is excruciatingly painful and evokes an intense and immediate physical reaction as well as an emotional response. We rub our feet where it hurts, we scream in pain, we move away from the spot to avoid experiencing the pain a second time. We also remember the spot on the floor […]
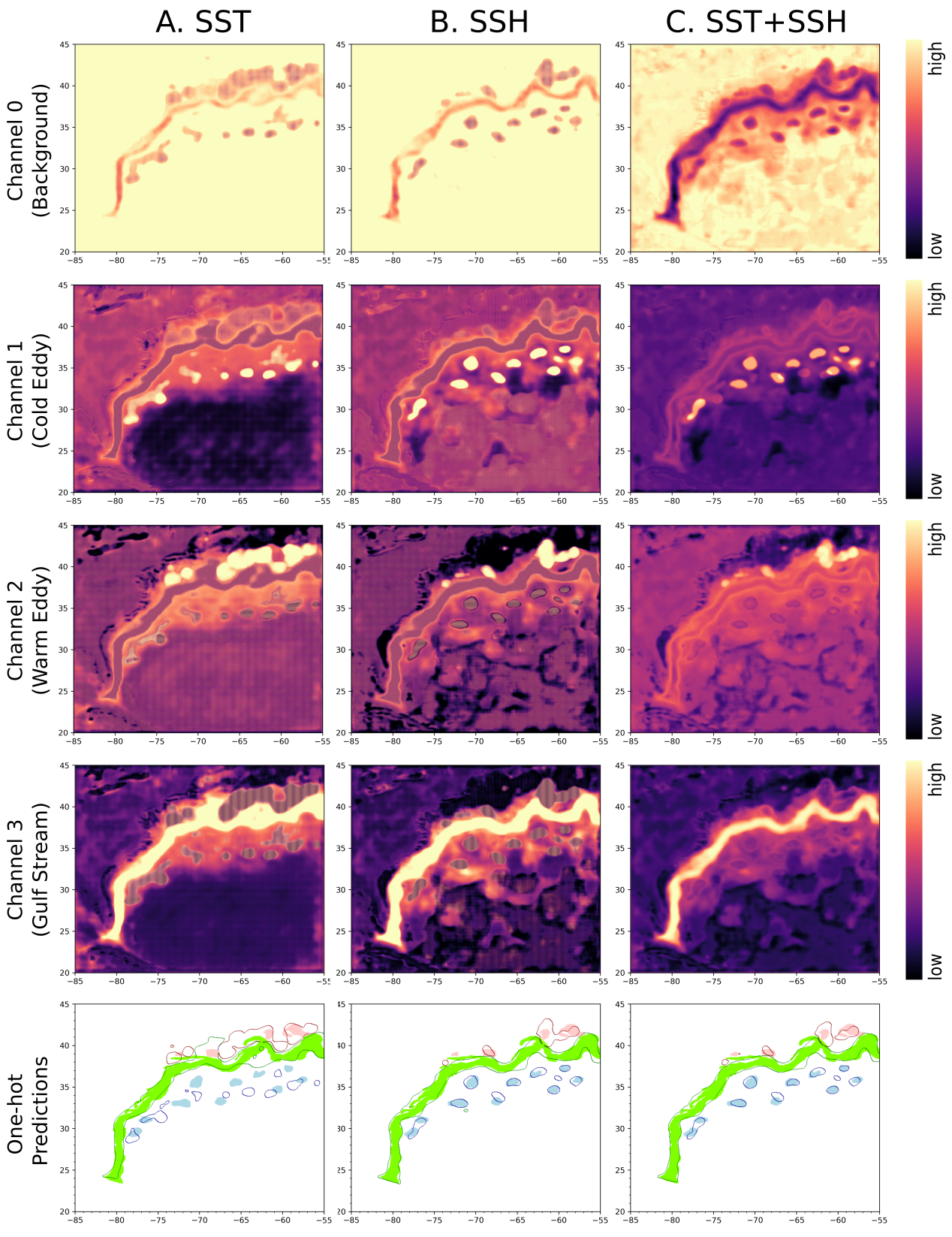
Deep Learning for Satellite Oceanography
We developed a W-Net architecture, a novel structure inspired from the classical U-Net architecture for semantic segmentation. Two U-net like branches are used, one for SST data and one for SSH data. The two branches give a segmentation with high accuracy for Gulf Stream and Rings. Using two parallel Encoder-Decoder networks (one branch for SST […]
Computation of Signals at synapses
Our group try to decipher real time molecular mechanisms that contribute to fidelity of signal processing at synapse. We combine nanobiology with imaging of stochastic processes at synapses at single molecule resolution using both conventional and neuromorphic detectors at nanoscale. Our goal is to generate realistic realtime nanoscale model to understand signal transmission at synapse. […]
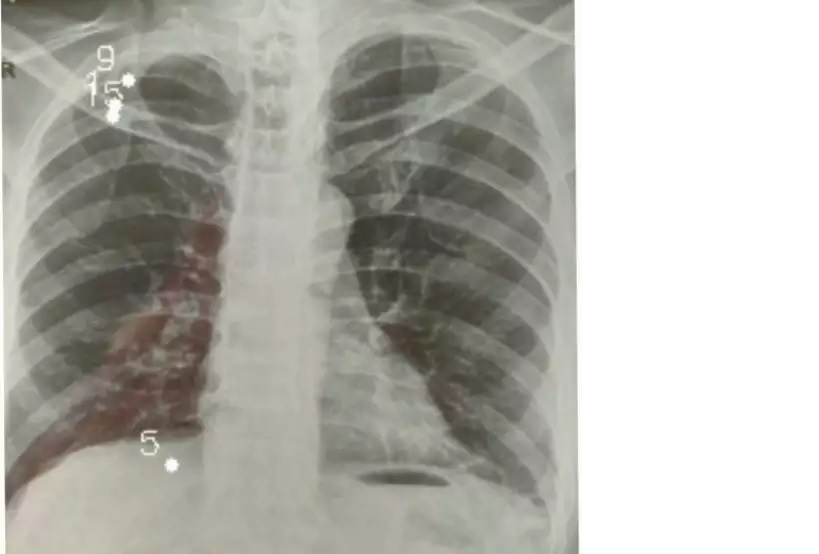
AI-driven XraySetu for early-Covid interventions over WhatsApp [Chiranjib Bhattacharyya, CSA]
The project was started by Dr. Geetha Manjunath of Niramai Health and Prof. Chiranjib Bhattacharyya of IISc, in the first wave of Pandemic to address the issue of Accessibility of Healthcare in the context of COVID-19. The key premise behind the project was X-rays are far more ubiquitous than RTPCR tests and a diagnostic tool based […]
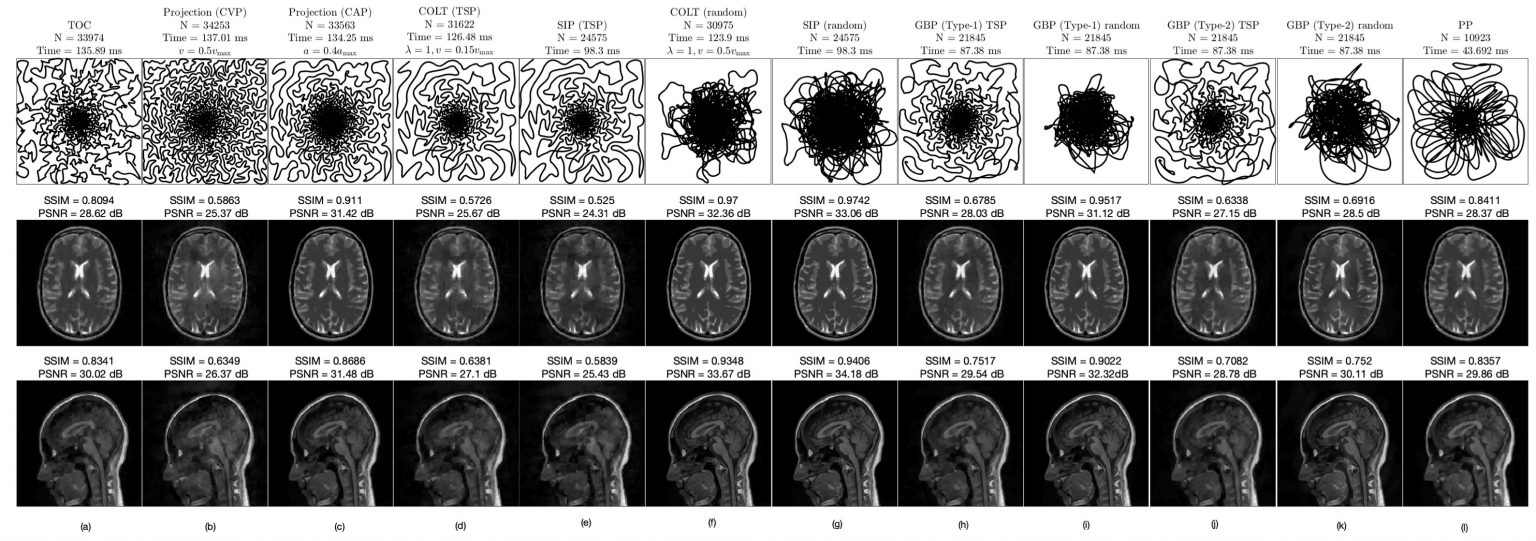
A generalized framework for projection-based methods for sampling in MRI systems [ K. V. S. Hari, ECE]
MRI collects samples in the Fourier domain, called as the k-space. The k-space is traversed along continuous trajectories using varying magnetic gradients. Limited by hardware and physiological factors such as gradient magnitude, gradient slew rate and MRI signal decay, long scan times are required to traverse the complete k-space. Scan time reduction in MRI is […]
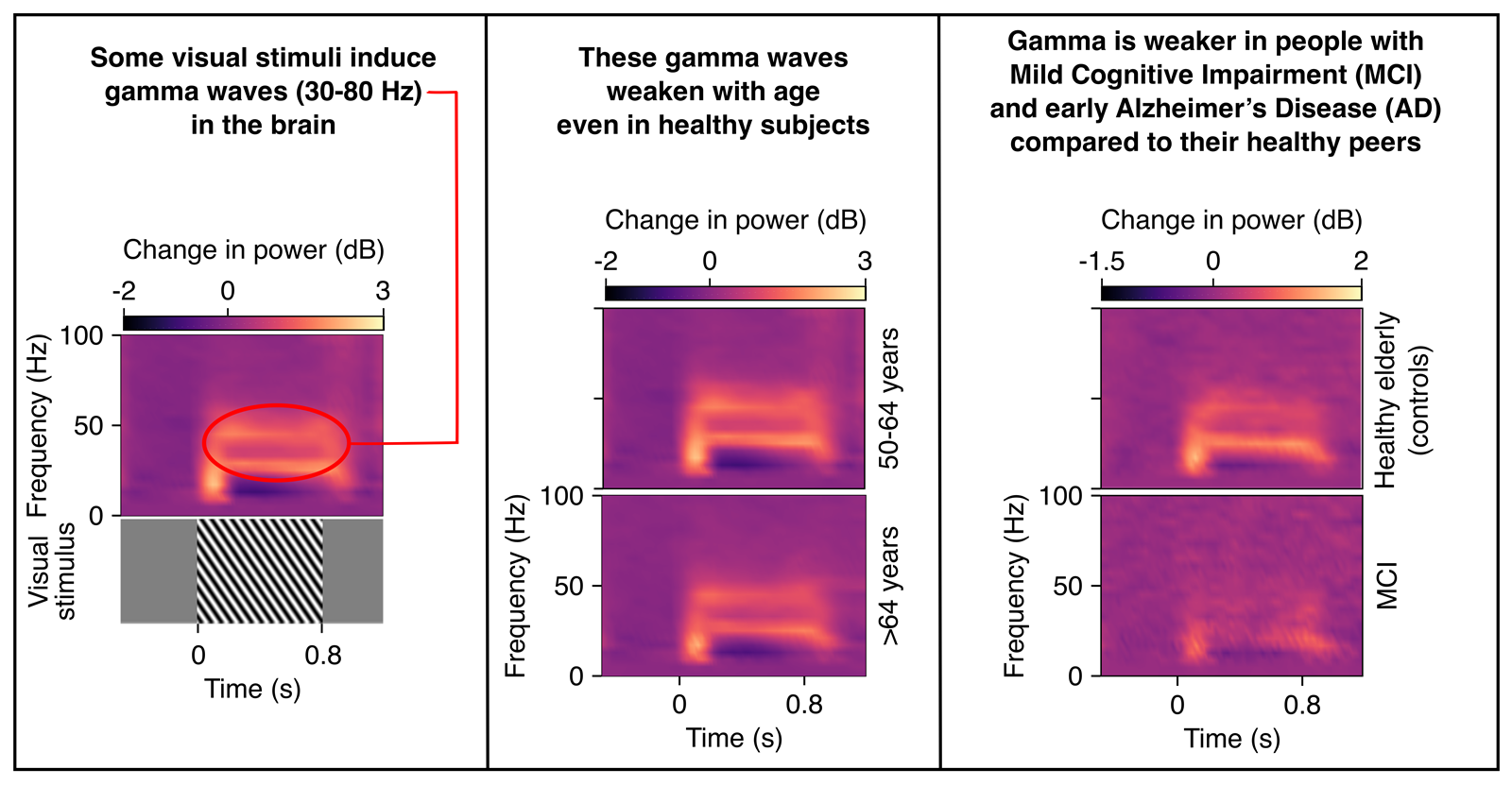
Gamma oscillations as a biomarker for early diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) [Supratim Ray, CNS]
Electrical signals recorded from the brain often show fluctuations between 30-80 Hz, which is called the gamma rhythm. These can be induced by simply viewing images with black and white patterns, called gratings. We recorded brain signals using a non-invasive technique called electroencephalogram (EEG) from ~250 elderly subjects while they viewed gratings, and found that […]
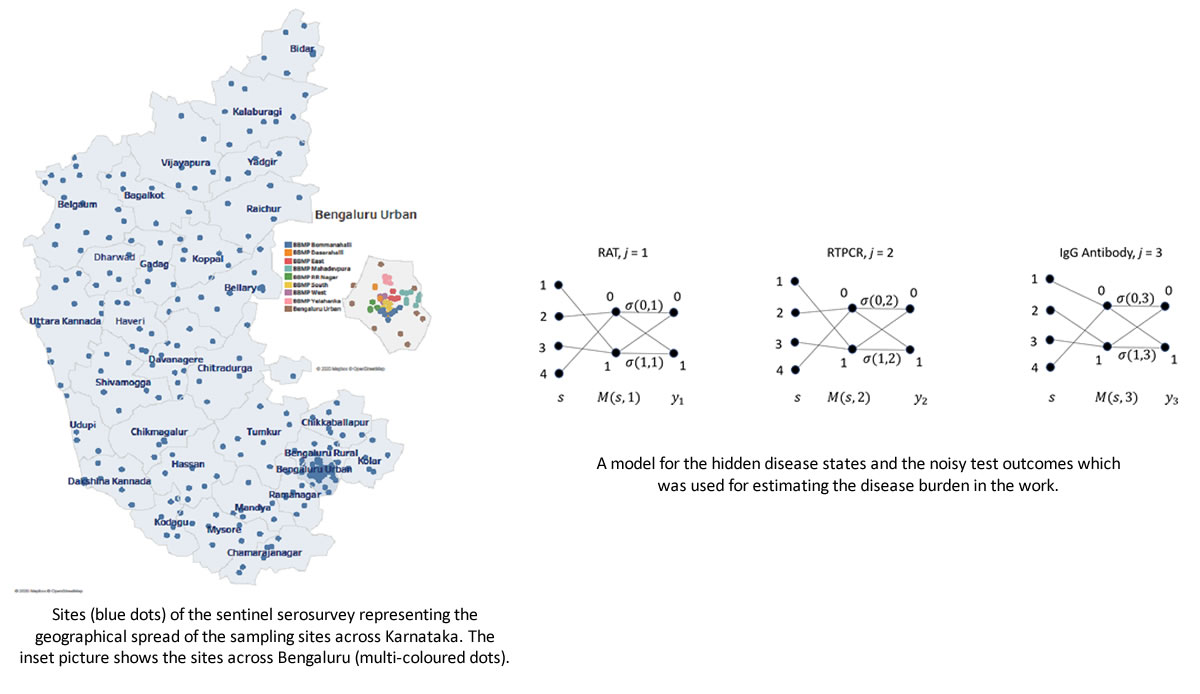
Estimating the COVID-19 burden in Karnataka [Rajesh Sundaresan, ECE]
This work, a Karnataka-wide COVID-19 serological survey, provided a wealth of information about the state of the pandemic. It enabled principled and data-driven public health responses (testing strategies, district-level response recommendations, etc.). It highlights how to leverage the existing public health infrastructure, gather useful local information, and shape targeted responses at the district/taluk level. It […]
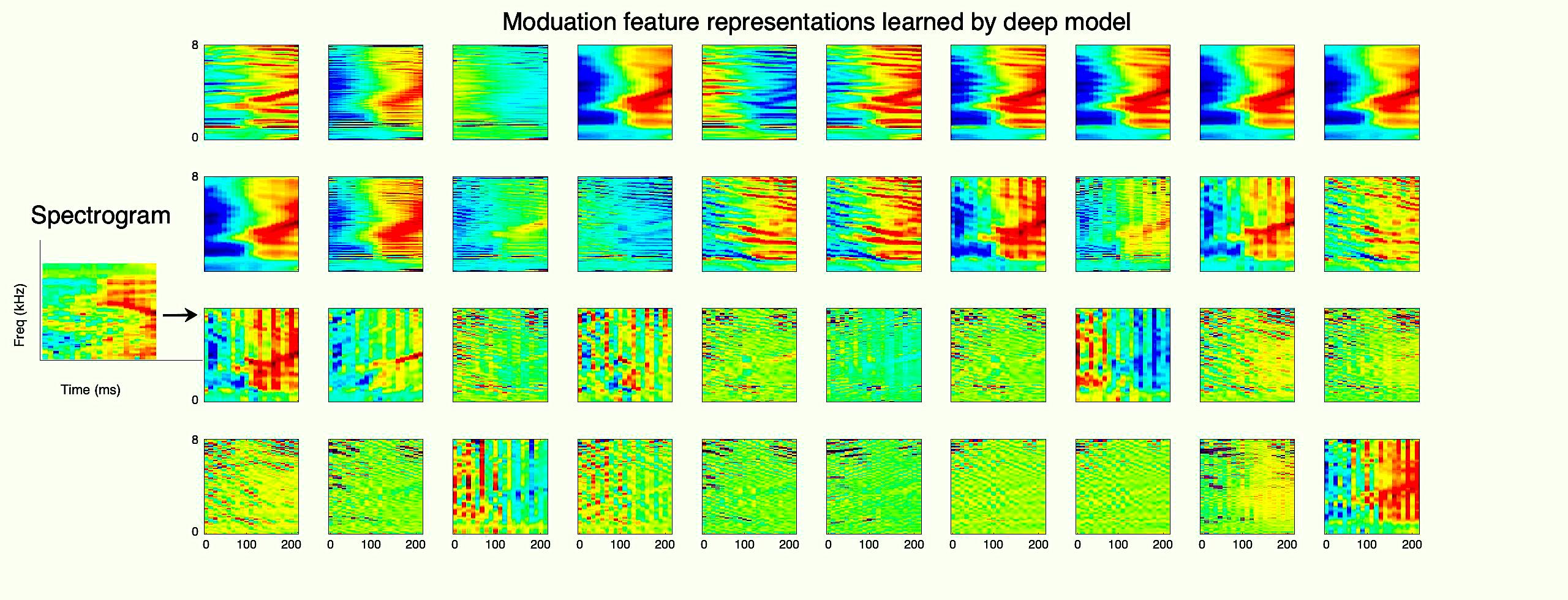
Deep Unsupervised Speech Representation Learning [Sriram Ganapathy, EE]
The performance of speech systems is degraded in the presence of noise. The principle of modulation filtering attempts to remove the spectro-temporal modulations that are susceptible to noise. While traditional approaches use modulation filters that are hand-crafted, we propose a novel method for modulation filter learning using deep variational models. Specifically, we pose the filter […]
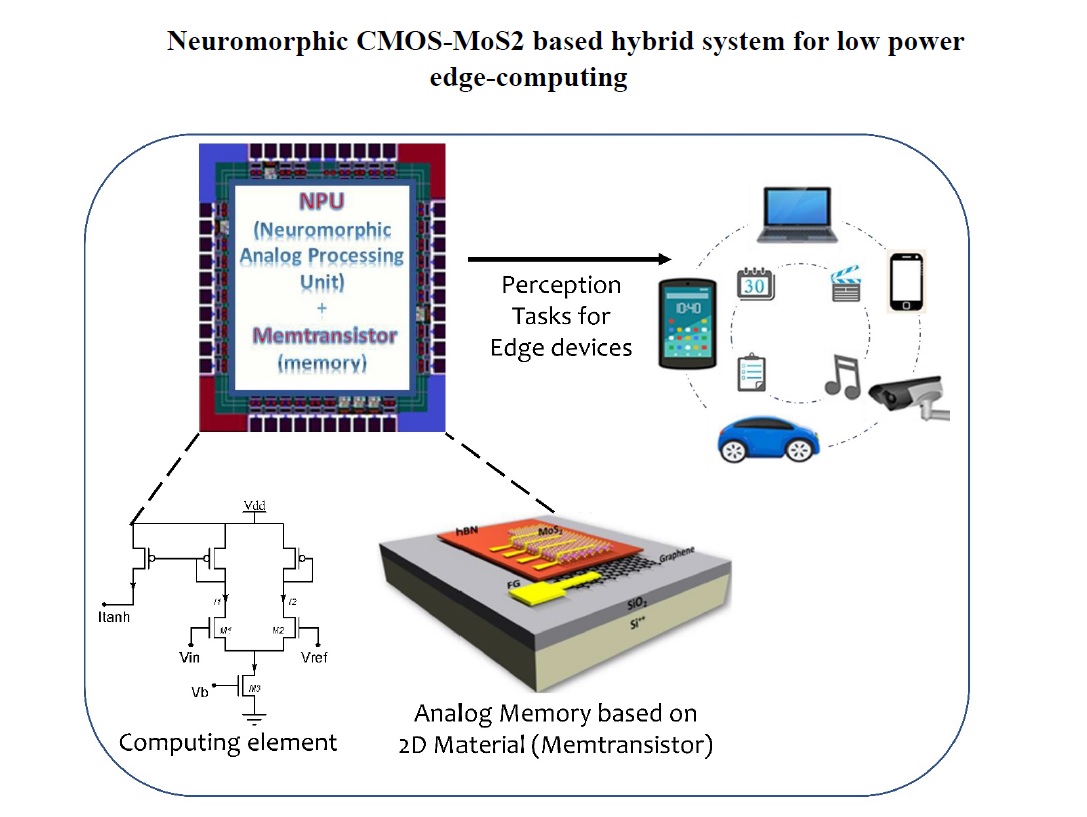
Neuromorphic CMOS-MoS2 based hybrid system for low power edge-computing [Chetan Singh Thakur, ESE]
The brain is an ideal template for next-generation computing architectures. We, at NeuRonICS lab IISc, have developed a hybrid architecture [1] that combines a silicon neuron, acting as the computing unit, with a 2D nanosheet of molybdenum sulphate, acting as a memristor that works like a synapse [2]. This can improve power use and performance […]
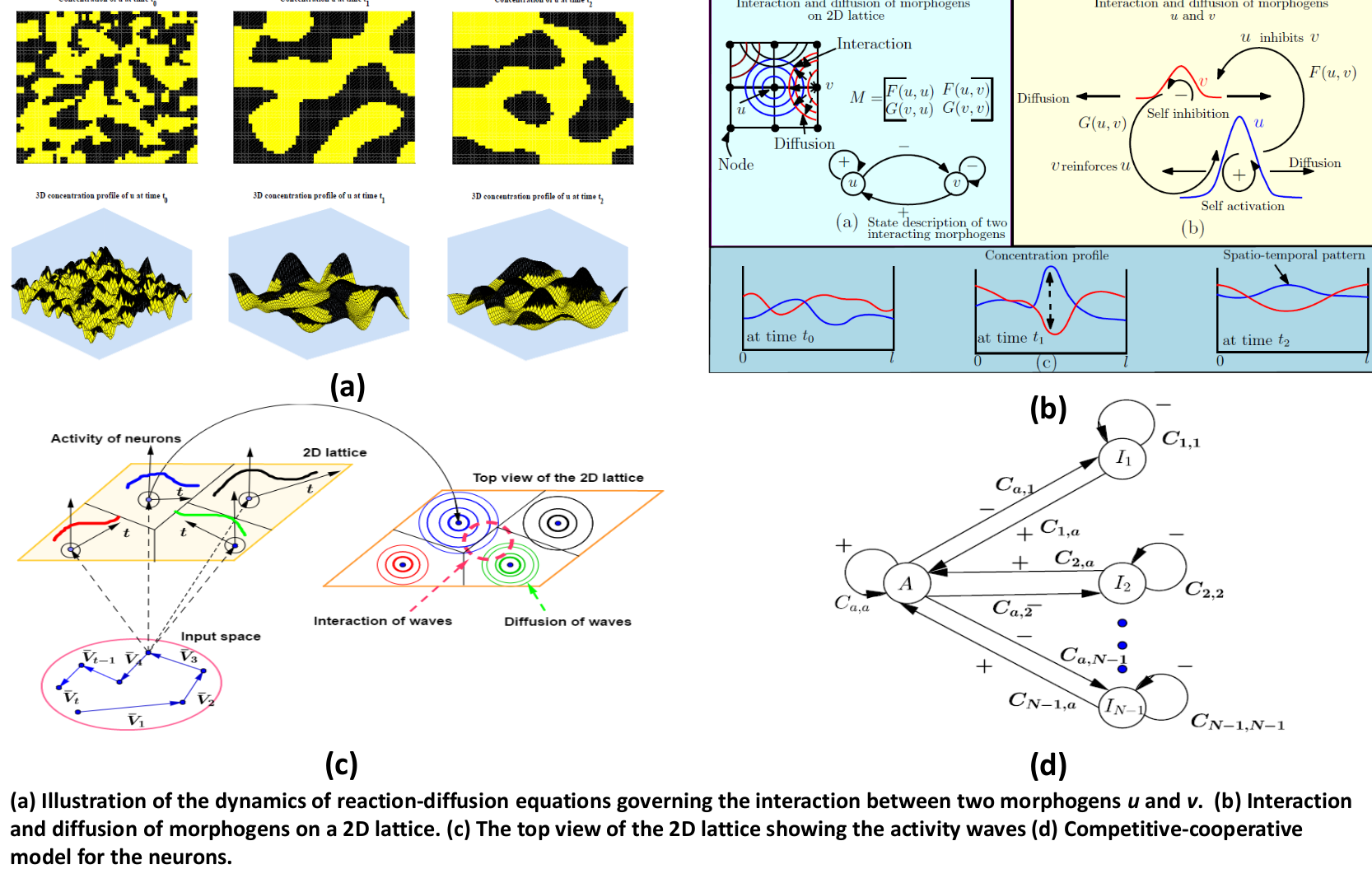
Temporal Self-Organization: A Reaction-diffusion Framework for Spatio-temporal Memories [Shayan Garani, ESE]
Self-organizing maps find numerous applications in learning, clustering and recalling spatial input patterns. The traditional approach in learning spatio-temporal patterns is to incorporate time on the output space of a self-organizing map along with heuristic update rules that work well in practice. Inspired by the pioneering work of Alan Turing, who used reaction-diffusion equations to […]
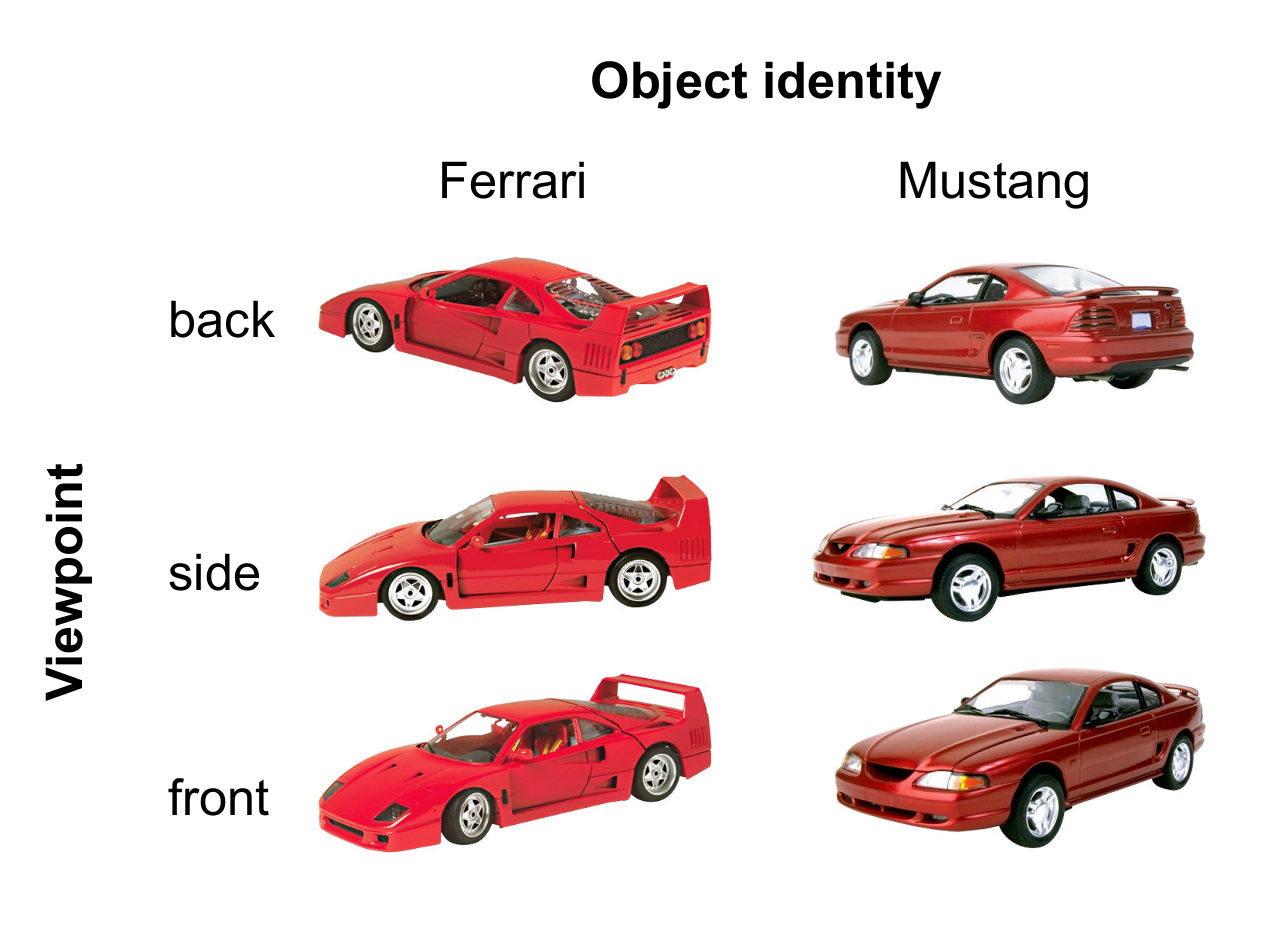
Multiplicative mixing of object identity and image attributes in single inferior temporal neurons [SP Arun, CNS]
Knowing a Ferrari from a Mustang from an image can be hard because one has to detect their unique features while ignoring large image variations due to changes in view, size, position etc. Successful recognition requires both object identity and image attributes to be represented efficiently but precisely how the brain does it has been […]
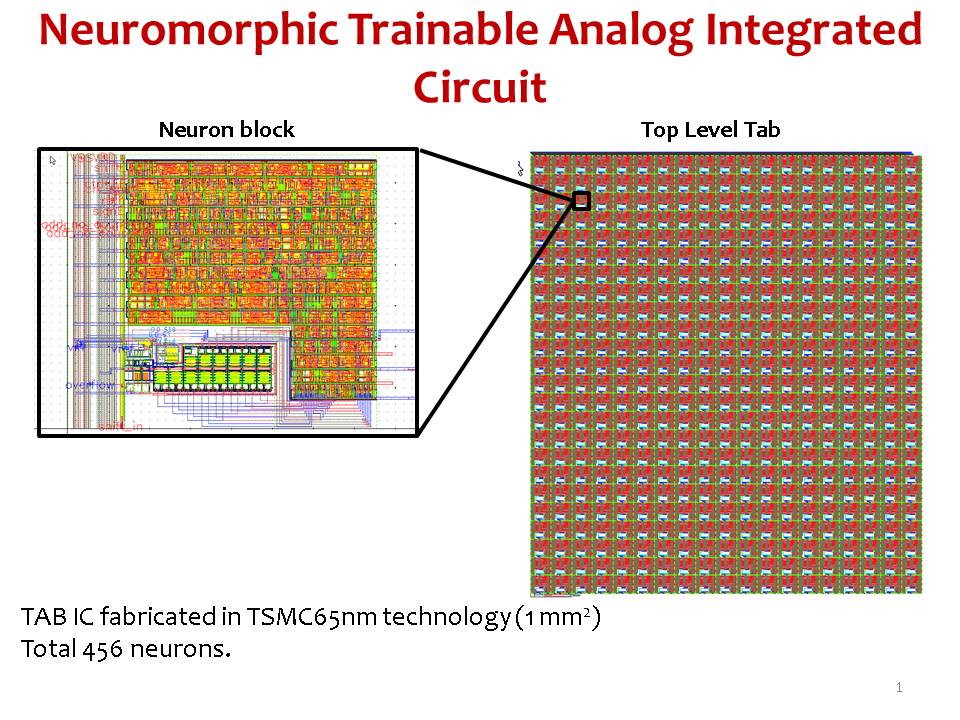
An Analogue Neuromorphic Co-Processor That Utilizes Device Mismatch for Learning Applications [Chetan Singh Thakur, ESE]
As the integrated circuit (IC) technology advances into smaller nanometre feature sizes, a fixed-error noise known as device mismatch is introduced owing to the dissimilarity between transistors, and this degrades the accuracy of analog circuits. We present an analog co-processor that uses this fixed-pattern noise to its advantage to perform complex computa- tion. This circuit […]
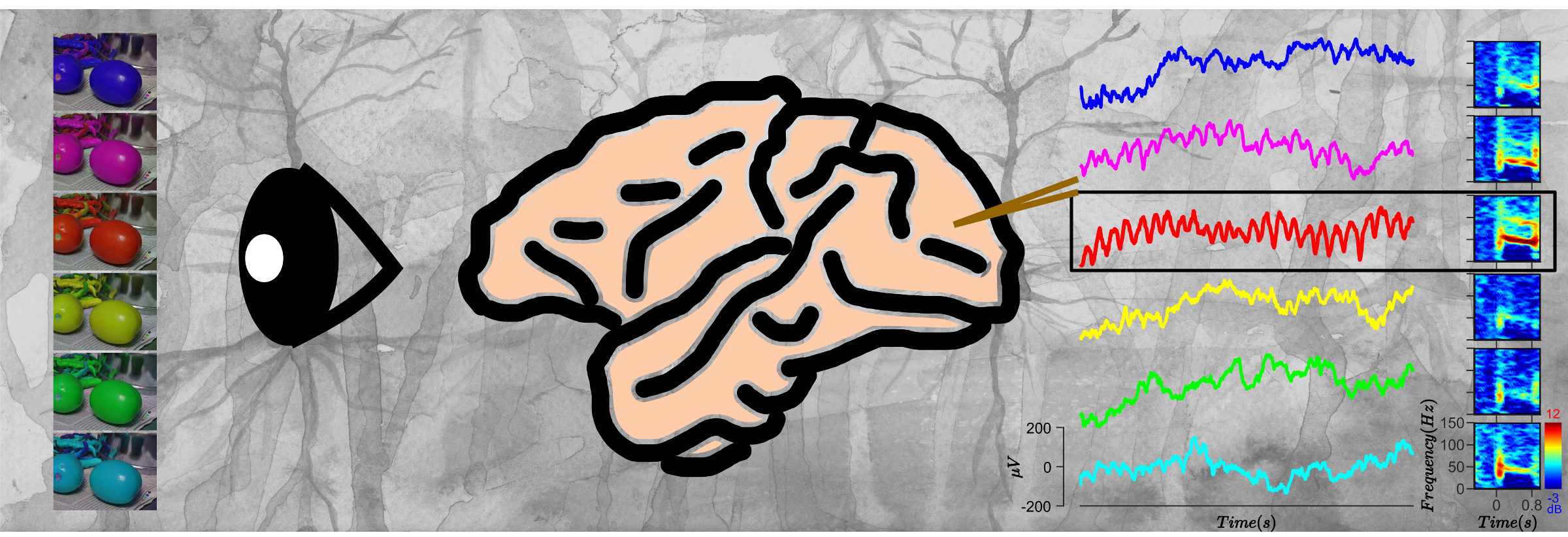
Red induces strong gamma oscillations in the brain [Supratim Ray, CNS]
What changes inside the brain when one sees a colourful flower as opposed to a grayscale version of it? How do the brain signals change when one sees a green jackfruit versus a red tomato? Does the redness of the tomato matter? We studied such questions by recording signals from the primary visual cortex (an […]
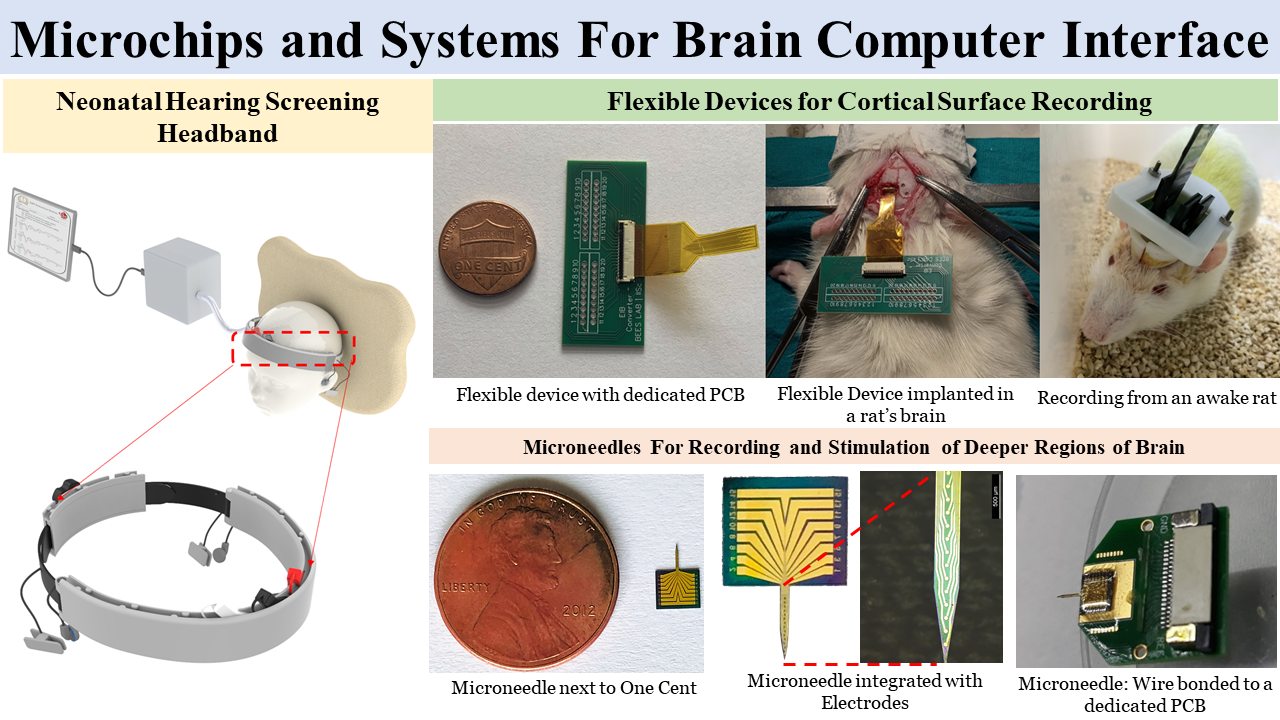
Microchips and Systems For Brain Computer Interface [Hardik J Pandya, DESE]
The BEES Lab, DESE, IISc focuses on developing microchip-based system solutions for screening, diagnostic, and therapeutic applications in neuroscience and neurophysiology. The group develops single and multi-shank silicon microneedles integrated with microelectrodes and related signal conditioning modules to record neural biopotentials and signals and electrical stimulation of deep brain regions. These microneedle-based systems find applications […]
Neural computations underlying cognition [Sridharan Devarajan, CNS and Govindan Rangarajan, Math]
How does our brain enable us to pay attention selectively to some things, and to ignore others? What happens in the brain when we make important decisions? Our research focuses on understanding the neural basis of cognitive phenomena such as selective attention and decision making. To address these questions, our group has developed quantitative approaches […]